Complete the following questions in your technology notebook. Work by yourself to answer the questions.
-
What did you find most interesting about Traci Morgan’s work? What parts of her work do you think you would enjoy?
-
Complete the following tasks in your technology notebook.
- Begin a personal glossary at the back of your technology notebook. Start by adding a definition of technology. Then, add a definition of doing technology. Hint
- How is the definition of technology in this activity similar to your team’s definition from the Engage activity?
- How is the definition in this activity different from your team’s definition?
-
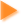
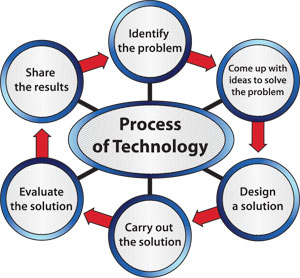 Figure 15: The process of doing technology. Why do you think the stages are shown in a circle?
Figure 15: The process of doing technology. Why do you think the stages are shown in a circle?Examine the picture in figure 15 that illustrates the process of doing technology. Why do you think the stages go in a circle instead of in a line?
-
Do you think there are limits on who can do technology? Why or why not?
-
In Steps 7 through 9, you used a strategy called TSAR to help you think about and revise your ideas.
- How was your partner important in this process?
- How did the TSAR strategy help you revise your ideas?
-
This activity is an Explain activity. In Explain activities, you are responsible for constructing an explanation of a concept.
- How were you responsible for explaining a concept in this activity? Hint
- How is this different from the way you might have learned science or technology before?
Answers to Reflect and Connect
-
What did you find most interesting about Traci Morgan’s work? What parts of her work do you think you would enjoy?
Students’ answers will vary. Research has shown that students are more motivated to learn when they see a connection of the content to their own lives. This question is meant to help them think about what aspects of engineering they might enjoy, which will motivate them to learn more.
-
Complete the following tasks in your technology notebook.
-
Begin a personal glossary at the back of your technology notebook. Start by adding a definition of technology. Then, add a definition of doing technology. Hint
A personal glossary is helpful to students, as it keeps information in a convenient place—their own technology notebooks. You may wish to have them start the glossary in the last 15 to20 pages of their notebooks. Another way to do this is to have them turn their technology notebooks upside down and backward, and then start the glossary on the first page facing this direction. Students should get in the habit of adding any words that are in bold or are unfamiliar to them. For the glossary, you may wish to have them not only write the word and the definition, but also draw a picture, write about how to pronounce the word, and list a personal connection or a way to remember the word. For example, if they learned the word termite, they might have an entry that looks like figure T2.
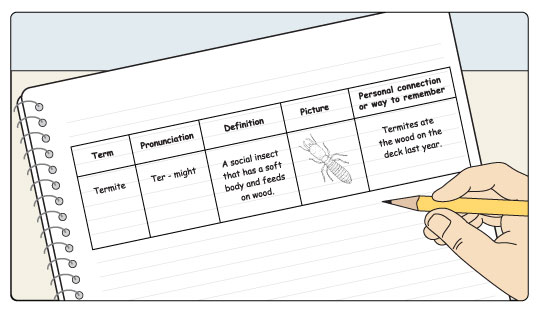 Figure T2: An example of a personal glossary entry. Decide how you would like your students to make entries in their personal glossaries. Although the word and a definition in their own words are helpful, you might also have them draw a picture, write about how to pronounce the word, and list a personal connection or a way to remember the word.
Figure T2: An example of a personal glossary entry. Decide how you would like your students to make entries in their personal glossaries. Although the word and a definition in their own words are helpful, you might also have them draw a picture, write about how to pronounce the word, and list a personal connection or a way to remember the word. -
How is the definition of technology in this activity similar to your team’s definition from the Engage activity?
Students should compare their team’s definition of technology to the definition in this activity. Their answers will vary depending on the definition the team wrote. They should try to identify at least one similarity.
-
How is the definition in this activity different from your team’s definition?
Students should compare their team’s definition of technology to the definition in this activity. Their answers will vary depending on the definition the team wrote. They should try to identify at least one difference.
-
-
Examine the picture in figure 15 that illustrates the process of doing technology. Why do you think the stages go in a circle instead of in a line?
It is important for students to realize that even though there are particular stages in the process of doing technology, engineers and other people who are designing solutions often go through the process more than once. They may also repeat stages if they discover that the current solution is not working.
-
Do you think there are limits on who can do technology? Why or why not?
By this point, students should realize that they, as middle school students, can do technology. This should help them realize that anyone can do technology, because anyone can work to solve problems to help people. If students begin to bring up many limitations, challenge them about whether the limitations actually prevent people from solving problems.
-
In Steps 7 through 9, you used a strategy called TSAR to help you think about and revise your ideas.
-
How was your partner important in this process?
Students may realize that their partners helped them by sharing new ideas. This realization will depend on the quality of feedback they received and whether their partners wrote the same information. They may not believe that partners were important other than for carrying out the strategy. This is acceptable at this point in the chapter; however, work to make sure that students are able to provide good feedback to one another.
-
How did the TSAR strategy help you revise your ideas?
The TSAR strategy is a metacognitive strategy that helps students think about the way they think and form ideas. Students should begin to see the value of this strategy because they will be able to revise and improve their answers. It will depend on their work with their partners, so they may not believe that this strategy has helped them yet. They should begin to understand that in science and technology, answers develop as new information arises. They may realize that having a partner with whom to share ideas is helpful for developing ideas, as is having an opportunity to share what they themselves are thinking.
-
-
This activity is an Explain activity. In Explain activities, you are responsible for constructing an explanation of a concept.
-
How were you responsible for explaining a concept in this activity? Hint
Students were responsible for explaining the concept because they were the ones who answered the questions about solving problems, and they then did the reading to be able to put their cards in order. There was no lecture from a teacher about the stages in the process of doing technology. Rather, students used their own knowledge and resources to develop their ideas.
-
How is this different from the way you might have learned science or technology before?
Students’ answers will vary depending on the types of science and technology courses they took previously. If students have mostly been in traditional classes, they may say that this way is more fun, it is more work, it requires more writing, it allows them to think, or that the teacher and their textbook did not just provide them with the answer.
-